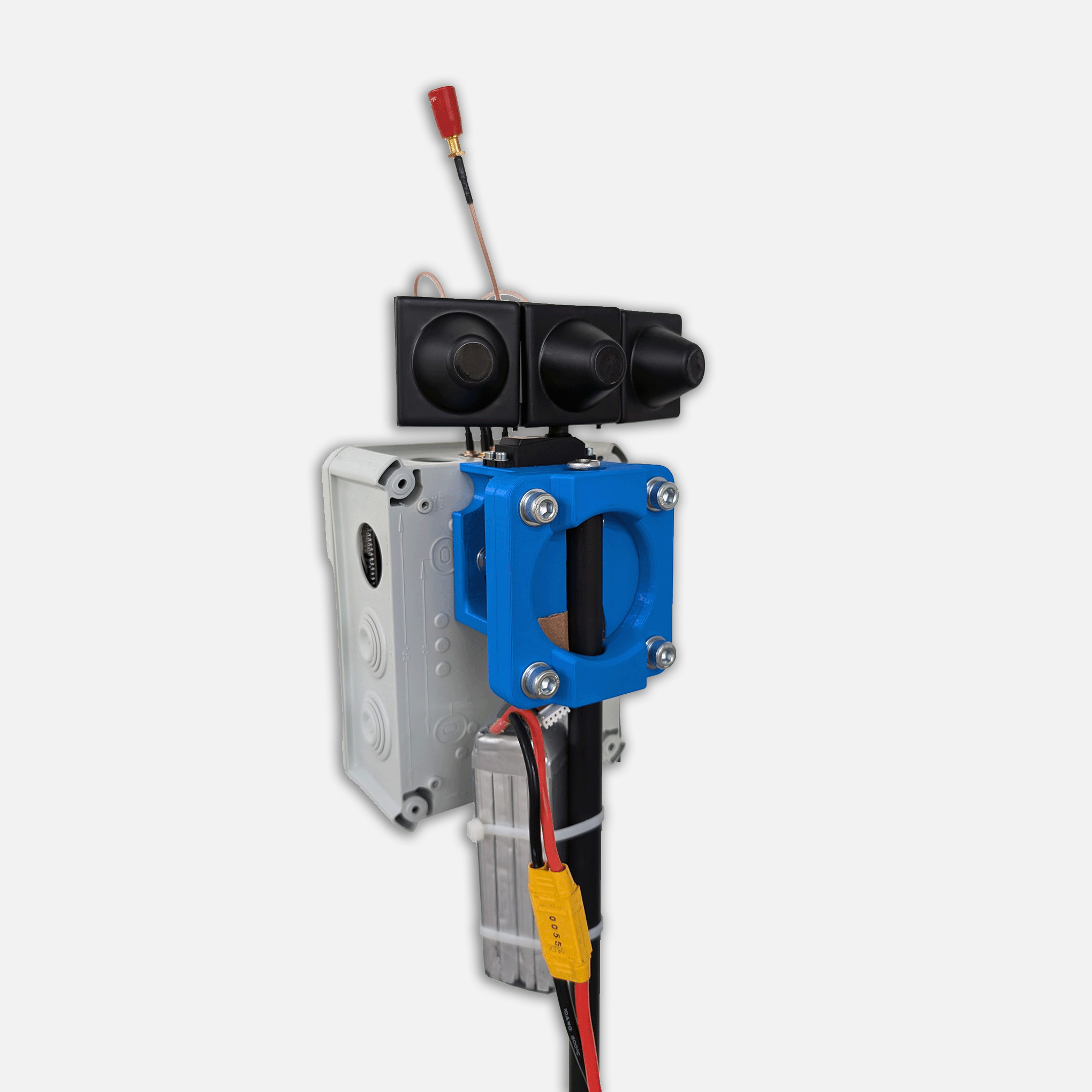
Custom drone design is an intricate process that transforms innovative ideas into sophisticated aerial platforms capable of solving real-world challenges. Whether you’re developing a drone for precision agriculture, industrial inspection, or specialized research, the journey from initial concept to successful flight involves multiple critical stages.
Understanding the Design Process
1. Defining Mission Requirements
Every custom drone begins with a fundamental question: What specific problem are we solving? This initial stage involves:
- Identifying precise operational needs
- Analyzing environmental constraints
- Determining performance specifications
- Establishing budget and technical limitations
Example Considerations
- Flight duration requirements
- Payload capacity
- Operating environment (temperature, altitude, terrain)
- Specific sensor or equipment integration needs
- Regulatory compliance expectations
2. Conceptual Design and Preliminary Engineering
Once mission requirements are clear, engineers develop initial design concepts. This phase involves:
- Selecting appropriate frame configurations
- Determining propulsion systems
- Calculating weight and balance
- Initial aerodynamic modeling
Common Frame
Configurations
- Quadcopter
- Hexacopter
- Fixed-wing hybrid
- Specialized mission-specific designs
3. Component Selection and Integration
Critical components that define a custom drone’s capabilities include:
1. Propulsion System
- Motor selection
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs)
- Battery technology
- Thrust-to-weight ratio calculations
2. Flight Control Systems
- Autopilot selection
- Sensor integration
- Communication module compatibility
- Redundancy and failsafe mechanisms
3. Payload Considerations
- Sensor weight and dimensions
- Power requirements
- Thermal management
- Vibration isolation
4. Advanced Simulation and Modeling
Before physical prototype construction, advanced computational tools allow engineers to:
- Simulate flight characteristics
- Test aerodynamic performance
- Predict system behaviors
- Identify potential design limitations
5. Prototype Development
The first physical manifestation of the design involves:
- 3D printing of structural components
- Modular component assembly
- Initial systems integration
- Preliminary ground testing
6. Rigorous Testing Phases
Comprehensive testing ensures design viability:
Ground Testing
- Static load measurements
- Electronic system verification
- Communication link stability
- Preliminary sensor calibration
Initial Flight Testing
- Controlled hover tests
- Basic maneuverability assessments
- Performance envelope exploration
- Safety system validation
7. Iterative Refinement
Custom drone design is rarely a linear process. Expect multiple design iterations based on:
- Test flight data
- Performance analysis
- Unexpected behavioral characteristics
- Emerging technological capabilities
Critical Design Considerations
Weight Optimization
- Utilize advanced composite materials
- Minimize unnecessary structural mass
- Balance durability with weight reduction
Power Management
- Implement efficient battery technologies
- Design intelligent power distribution systems
- Create redundant power pathways
Communication Resilience
- Multi-SIM communication modules
- Active antenna tracking
- Robust encryption and security protocols
Regulatory Compliance
Successful custom drone design must navigate:
- FAA regulations
- Local aviation restrictions
- Industry-specific operational guidelines
- Safety certification processes
Emerging Design Trends
- Increased autonomous capabilities
- Enhanced AI integration
- Modular, mission-adaptable platforms
- Improved energy efficiency
- Advanced sensor miniaturization
Conclusion
Custom drone design represents a sophisticated blend of engineering disciplines: aerodynamics, electronics, materials science, and mission-specific requirements. Success demands not just technical expertise, but a holistic understanding of operational contexts and emerging technological possibilities.
As drone technology continues to evolve, the ability to create precisely tailored aerial platforms will become increasingly valuable across industries.